Send from CLI
Bitwarden Send is available as a set of fully-featured CLI commands. This article documents the breadth of bw send commands, however Send is not a separate tool from the Bitwarden command-line Interface (CLI). Therefore, many of the commands, options, and concepts in the CLI documentation are relevant here.
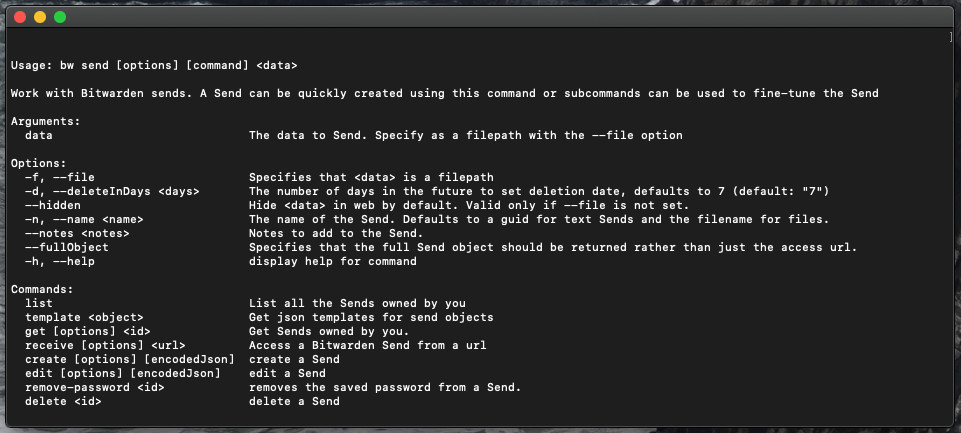
send
The send command is the master command used to access all Send-related subcommands:
Bashbw send [options] [command] <data>The send command can also be used as a shortcut to quickly create a Send, for example:
Bashbw send "Fastest Send in the West."will create a text Send with the contents Fastest Send in the West. and output the Send link. Or, for example:
Bashbw send -f <path/to/file.ext>will create a file Send with the specified file at the specified path and output the Send link.
Options:
Use
-n <name>or--name <name>to specify a name for the Send. If none is specified, name will default to theidfor text Sends and file name for file Sends. For multi-word names, use quotations"<name>".Use
-d <days>or--deleteInDays <days>to specify a deletion date for the Send (defaults to seven days if unspecified).Use
--maxAccessCountor-ato specify the maximum access count for the Send.Use
--hiddento specify that a text Send require recipients to toggle visibility.Use
--notes <notes>to add private notes to the Send. For multi-word notes, use quotations"<notes>".Use
--fullObjectto output the full Send object as JSON rather than only the Send link (pair this option with the--prettyoption for formatted JSON).
Full example:
Bashbw send -n "My First Send" -d 7 --hidden "The contents of my first Send."create
The create command creates a Send. create allows more advanced configuration than using only bw send and takes encoded JSON for its argument:
Bashbw send create [options] <encodedJson>A typical workflow might look something like:
Use the
templatecommand (see details) to output the appropriate JSON template for your Send type.Use a command-line JSON processor like jq to manipulate the outputted template as required.
Use the
encodecommand (see details) to encode the manipulated JSON.Use the
createcommand to create a Send from the encoded JSON.
For example, to create a text Send:
Bashbw send template send.text | jq '.name="My First Send" | .text.text="Secrets I want to share."' | bw encode | bw send createFor example, to create a password-protected file Send:
Bashbw send template send.file | jq '.name="My File Send" | .type=1 | .file.fileName="paperwork.png" | .password="p@ssw0rd"' | bw encode | bw send createFor example, to create a password-protected file Send with an explicit deletion date. This example is broken out by operating system due to the way .deletionDate= should be specified:
Bash$delDate = (Get-Date).AddDays(14) | date -UFormat "%Y-%m-%dT%H:%M:%SZ"
bw send template send.text | jq ".name=\`"My Send\`" | .text.text=\`"Secrets I want to share.\`" | .password=\`"password\`" | .deletionDate=\`"$delDate\`"" | bw encode | bw send createNotice in this example that the jq invocation must be wrapped in double quotes (" ") and use escapes (\) for each filter due to a nested date variable that configures a .deletionDate in the send.
Options:
Use
--file <path>to specify the file to Send (this can also be specified in encoded JSON).Use
--text <text>to specify the text to Send (this can also be specified in encoded JSON).Use
--hiddento specify that a text Send require recipients to toggle visibility.Use
--password <password>to specify the password needed to access password-protected.Use
--fullObjectto output the full Send object as JSON rather than only the Send link (pair this option with the--prettyoption for formatted JSON).
get
The get command will retrieve a Send owned by you and output it as a JSON object. get takes an exact id value or any string for its argument. If you use a string, get will search your Sends for one with a value that matches:
Bashbw send get [options] <id / string>If you create a Send in another Bitwarden app while this session is still active, use the bw sync command to pull recent Sends. For more information, refer to our CLI documentation.
Options:
Use
--textto output only the text contents of a text Send.Use
--fileto output only the file of a file Send. Pair--filewith--outputto specify a directory, or with--rawto output to stdout.Use
--output <output>to specify the output directory for the--fileoption.
edit
The edit command edits an existing Send. edit takes encoded JSON for its argument:
Bashbw send edit <encodedJson>A typical workflow might look something like:
Use the
getcommand (see details) to retrieve the desired Send according to its<id>.Use a command-line JSON processor like jq to manipulate the retrieved Send as required.
Use the
encodecommand (see details) to encode the manipulated JSON.Use the
editcommand to write the edits to the send.
For example:
Bashbw send get <id> | jq '.name="New Name" | .password=null' | bw encode | bw send editOptions:
Use
--itemid <itemid>to overwrite the id value provided of the Send with a new one.
note
You can't edit a file Send's file. To do this, you will need to delete the Send and re-create it with the appropriate file.
list
The list command will list all Sends owned by you and output them as JSON:
Bashbw send list [options]If you create a Send in another Bitwarden app while this session is still active, use the bw sync command to pull recent sends. For more information, refer to our CLI documentation.
Options:
Use
--prettyto format the JSON the output.Pipe stdout to a file using the
>operator, for example:Bashbw send list --pretty > /Users/myaccount/Documents/pretty_list_of_sends.json
delete
The delete command will delete a Send owned by you. delete takes only an exact id value for its argument.
Bashbw send delete <id>tip
If you don't know the exact id of the Send you want to delete, use bw send get <search term> to find it.
template
The template command returns the expected JSON formatting for a Send object. template takes an <object> specification for its argument, either send.text or send.file.
Bashbw send template <object>While you can use template to output the format to your screen, the most common use-case is to pipe the output into a bw send create operation, using a command-line JSON processor like jq and bw encode to manipulate the values retrieved from the template, for example:
Bashbw send template send.text | jq '.name="My First Send" | .text.text="Secrets I want to share."' | bw encode | bw send createreceive
The receive command accesses a Send. receive takes a Send <url> for its argument:
Bashbw send receive [options] <url>For text Sends,
receivewill return the text contents of the Send.For file Sends,
receivewill download the file to the current working directory.
Options:
Use
--password <password>to provide the password needed to access password-protected Sends as a string.Use
--passwordenv <passwordenv>to specify the password needed to access password-protected Sends as a stored environment variable.Use
--passwordfile <passwordfile>to specify the password needed to access password-protected Sends as a file with the password as its first line.Use
--objto output the full Send object as JSON rather than only the Send link (pair this option with the--prettyoption for formatted JSON).Use
--ouput <output>to specify the output directory for the contents of a file Send.